Hooks
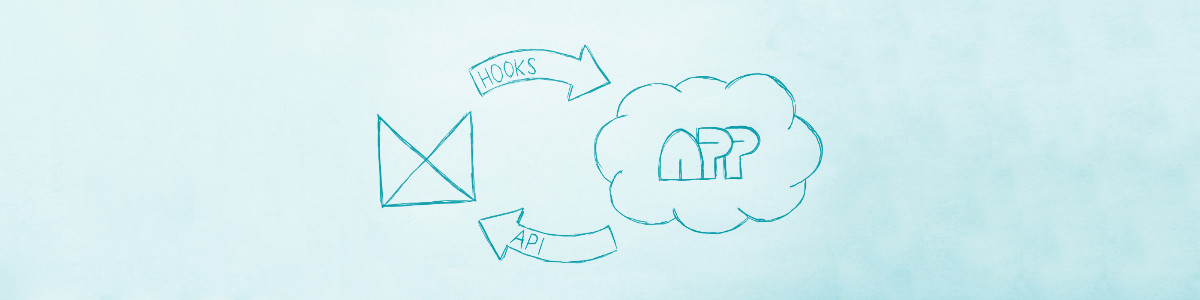
What is a hook?
Your app communicates with Mergado via our API. In exchange, Mergado also needs to actively communicate with your app.
This is done via web hooks, which Mergado - at certain situations - calls upon your app’s hook endpoints. To be specific, these hooks are HTTP POST requests with certain JSON (content type application/json) payload that specifies the hook’s nature.
Example
Imagine a situation, where an app is being turned off by its user. Typically, the app might have created a bunch of rules, elements and other “soon-to-be-unwanted-garbage” during the time it was enabled. This is one of the typical use cases for hooks - and in our example, it’s up to the developer of the app to clean up this built-up garbage.
| What Mergado sends | Its meaning | What your app should do |
|---|---|---|
|
Someone disabled your app for shop 42.
|
Use Mergado API to clean up after your app. You might want to erase rules, queries, elements, etc. it created during its lifetime. You also might want to make a note that your app no longer needs to run CRON jobs for this e-shop (as it would be pointless to do from now on), etc. Generally speaking, this is the time for cleaning up both Mergado and also your app's database. |
Data
The specific data along with a hook are entirely up to the type of the hook that is being called. Thus, any logic that handles a hook should assume data structure based solely on hook’s action field.
{
"action": "app.enable",
"entity_id": 42,
"entity_type": "shop",
"user_id": 234,
"user_locale": "cs_CZ"
}
Here, as an example, because the field action contains app.enable, we can now safely assume that data will also contain fields entity_id and entity_type. We know that Mergado is calling this hook because someone enabled your app for e-shop with ID 42.
You can find the list of all hooks along with their possible data fields down below.
Response
A hook is considered properly handled if Mergado receives back a 2xx HTTP response. Hooks returning a 4xx HTTP response are considered to be handled improperly and that can either be evaluated as an error or can be safely ignored by Mergado, based on the nature of the hook. Lastly, a hook is considered to be erroneous when there is 5xx HTTP response and such situations are always considered an error.
Security
Every time Mergado sends a hook, the request will contain a special HTTP header Mergado-Apps-Webhook-Secret with a specific secret string that is unique to each app and each of its envs. This is true for all webhooks and for all app-rule based requests, too.
You can find all of your app’s webhook secret values in Developers.
List of hooks
Below is the list of currently implemented hooks that can be invoked on your app by Mergado.
ping
A test hook that can be sent from app’s Developers page. This hook is successfully handled when the app returns a HTTP response 2xx and a JSON containing field message with the value of pong.
| Hook | OK response | Error response |
|---|---|---|
|
|
|
app.enable
Called when app is being enabled. If this hook is properly handled (i.e. app returns HTTP code 2xx), app is going to be enabled. Otherwise (HTTP codes 4xx or 5xx) the app is not allowed to be enabled. If such cases optional JSON with a message field can be returned and this message will be then reported back to the user (eg. reasons why the app currently cannot be enabled).
Parameters
entity_id: ID of entity (based on type) for which the app is being enabled.entity_type: Type of entity. Values can beuser,shoporproject.user_id: ID of the user enabling this app.user_locale: Locale of the user enabling the app, e.g.cs_CZ,sk_SK,en_GB, etc.
Example
| Hook | OK response | Error response |
|---|---|---|
|
|
|
app.disable
Called when app is being disabled. If this hook is properly handled (i.e. app returns HTTP code 2xx), app is going to be disabled. Otherwise (HTTP codes 4xx or 5xx) the app is not allowed to be disabled. If such cases optional JSON with a message field can be returned and this message will be then reported back to the user (eg. reasons why the app currently cannot be disabled).
Parameters
entity_id: ID of entity (based on type) for which the app is being disabled.entity_type: Type of entity. Values can beuser,shoporproject.user_id: ID of the user disabling this app.user_locale: Locale of the user disabling the app, e.g.cs_CZ,sk_SK,en_GB, etc.
Example
| Hook | OK response | Error response |
|---|---|---|
|
|
|
Process hooks
process.import.start
Event hook called when Mergado is about to start import process of a project. ¹ ²
| Hook |
|---|
|
process.import.finish
Event hook called when Mergado finished project’s import process. ¹ ²
| Hook |
|---|
|
process.import.failed
Event hook called when a rule crashes within a project. ¹ ²
| Hook |
|---|
|
process.apply.start
Event hook called when is about to start apply process of a project. ¹ ²
| Hook |
|---|
|
process.apply.finish
Event hook called when finished project’s apply process. ¹ ²
| Hook |
|---|
|
process.export.start
Event hook called when is about to start export process of a project. ¹ ²
| Hook |
|---|
|
process.export.finish
Event hook called when finished project’s export process. ¹ ²
| Hook |
|---|
|
Project control hooks
control.project.disabled
Event hook called when a project is being disabled. ¹ ²
| Hook |
|---|
|
control.project.enabled
Event hook called when a project is being enabled. ¹ ²
| Hook |
|---|
|
control.project.deleted
Event hook called when a project is being deleted. ¹ ²
| Hook |
|---|
|
control.project.settings_changed
Event hook called when a change in project’s settings was detected. ¹ ²
| Hook |
|---|
|
Project elements control hooks
control.project.element_created
Event hook called when a user creates an element in a project. ¹ ²
| Hook |
|---|
|
control.project.element_edited
Event hook called when a user edits an element in a project. ¹ ²
| Hook |
|---|
|
control.project.element_deleted
Event hook called when a user deletes an element in a project. ¹ ²
| Hook |
|---|
|
Project queries control hooks
control.project.query_created
Event hook called when a user creates and saves a query in a project. ¹ ²
| Hook |
|---|
|
control.project.query_edited
Event hook called when a user edits a query in a project. ¹ ²
| Hook |
|---|
|
control.project.query_deleted
Event hook called when a user deletes a query in a project. ¹ ²
| Hook |
|---|
|
Project rules control hooks
control.project.rule_created
Event hook called when a user creates a rule in a project. ¹ ²
| Hook |
|---|
|
control.project.rule_edited
Event hook called when a user edits a rule in a project. ¹ ²
| Hook |
|---|
|
control.project.rule_deleted
Event hook called when a user deletes a rule in a project. ¹ ²
| Hook |
|---|
|
JSON list of all above
[
"ping",
"app.enable",
"app.disable",
"process.import.start",
"process.import.finish",
"process.apply.start",
"process.apply.finish",
"process.apply.failed",
"process.export.start",
"process.export.finish",
"control.project.enabled",
"control.project.disabled",
"control.project.deleted",
"control.project.settings_changed",
"control.project.element_created",
"control.project.element_edited",
"control.project.element_deleted",
"control.project.query_created",
"control.project.query_edited",
"control.project.query_deleted",
"control.project.rule_created",
"control.project.rule_edited",
"control.project.rule_deleted"
]
References:
¹ - The response of your app is ignored.
² - This event is currently sent only to project and eshop apps.